What is Heartache?
Heartache, often described as chest discomfort or pain, arises when the heart muscle doesn’t receive sufficient oxygen. Medically termed angina, this condition is a warning sign that the heart is struggling to meet the body’s demands.
The heart is a vital organ responsible for pumping oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. To function efficiently, it requires its own steady supply of oxygen. When this supply is compromised—due to narrowed or blocked arteries—the heart muscle reacts with pain.
Heartache typically manifests as a pressing, squeezing, or burning sensation in the chest, often concentrated behind the breastbone or on the left side. It commonly occurs during physical exertion or stress and eases with rest.
Heartache is frequently linked to coronary artery disease, where plaque buildup narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow. However, it can also stem from other conditions like:
- Heart valve diseases
- Heart muscle infections
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats)
- Heart failure
Since heartache can signal serious underlying issues, seeking medical attention is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What Are the Causes of Heart Pain?
Heart pain arises from various conditions that disrupt the heart’s oxygen supply. Below are the primary causes:
Coronary Artery Disease
The most common cause, where narrowed or blocked coronary arteries reduce blood flow to the heart.
Stable Angina
Predictable chest pain triggered by physical activity or stress, relieved by rest.
Unstable Angina
Sudden, severe pain that occurs even at rest, often a precursor to a heart attack.
Coronary Artery Spasm
Temporary tightening of the coronary arteries, cutting off blood flow momentarily.
Arrhythmia
Irregular heart rhythms that strain the heart, leading to pain.
Other Causes
Conditions like heart valve disorders, infections, or heart failure can also induce heart pain.
What Are the Symptoms of Heart Pain?
Heart pain symptoms often emerge during physical or emotional stress and may include:
Burning or Aching Sensation
A mild to severe discomfort in the chest, sometimes mistaken for indigestion.
Radiating Pain
The pain may spread to the left arm, shoulder, neck, jaw, or back.
Shortness of Breath
Difficulty breathing, especially during exertion.
Excessive Sweating
Cold, clammy sweat without physical exertion.
Nausea or Vomiting
A queasy feeling, sometimes accompanied by vomiting.
Fatigue and Weakness
Unexplained exhaustion, even after minimal activity.
How to Recognize Heart Pain?
Heart pain is typically described as a heavy pressure or tightness in the chest, lasting a few minutes to 15 minutes. It often coincides with other symptoms like breathlessness, dizziness, or sweating.
Where Is Heart Pain Felt?
Primarily located in the chest (behind the breastbone or left side), it can radiate to the arms, shoulders, neck, or back.
How Is Heart Pain Diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis is essential, as heart pain can mimic other conditions. Common diagnostic methods include:
Medical History and Physical Exam
A doctor evaluates symptoms, listens to the heart, and checks vital signs.
Electrocardiography (ECG)
Measures the heart’s electrical activity to detect irregularities.
Stress Test
Monitors heart performance during exercise to identify exertion-related issues.
Blood Tests
Checks for cardiac enzymes like troponin, which rise during heart muscle damage.
Chest X-ray
Reveals heart size, lung fluid, or other abnormalities.
Echocardiography
Uses ultrasound to assess heart structure and function.
Coronary Angiography
A dye-enhanced X-ray to visualize blocked or narrowed arteries.
How Is Heart Pain Treated?
Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and improving heart health through:
Medications
- Nitrates (expand blood vessels)
- Beta-blockers (reduce heart rate and blood pressure)
- Calcium channel blockers (relax arteries)
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Heart-healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Smoking cessation
- Limited alcohol intake
Medical Procedures
- Stent placement to open blocked arteries
- Coronary angioplasty to widen narrowed vessels
Heart Pain vs. Chest Pain
While heart pain (angina) stems from reduced oxygen to the heart, chest pain can arise from non-cardiac issues like:
- Respiratory problems
- Digestive disorders (e.g., acid reflux)
- Muscle or bone injuries
- Anxiety or stress
Key Difference: Heart pain is usually centralized (left chest/breastbone), while other chest pains vary in location.
Heart Pain in Children
Though rare, children may experience heart pain due to:
- Musculoskeletal growth pains (often mistaken for heart pain)
- Congenital heart defects
- Infections (e.g., rheumatic fever)
- Stress or overexertion
Symptoms in Children:
- Chest pressure or tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or fainting
A pediatrician should evaluate persistent symptoms, possibly ordering an ECG or echocardiogram.
Psychological Heartache
Stress or anxiety can mimic heart pain, causing:
- Chest tightness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Sweating or dizziness
Treatment: Therapy (e.g., cognitive behavioral therapy) and stress management techniques.
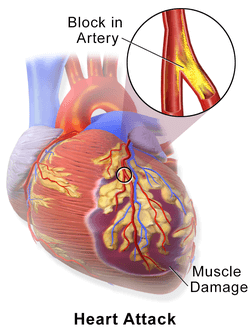
Heart Pain vs. Heart Attack
- Heart pain (angina): Temporary, triggered by exertion, relieved by rest.
- Heart attack: Sudden, severe, and persistent due to blocked blood flow.
Heart attack symptoms:
- Crushing chest pain
- Cold sweats
- Nausea/vomiting
- Fainting
Immediate medical care is critical during a heart attack.
Conclusion
Heartache is a serious symptom that warrants medical attention. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help manage the condition effectively. Lifestyle changes, medications, and timely interventions play key roles in maintaining heart health. Always consult a doctor for persistent or severe chest pain.